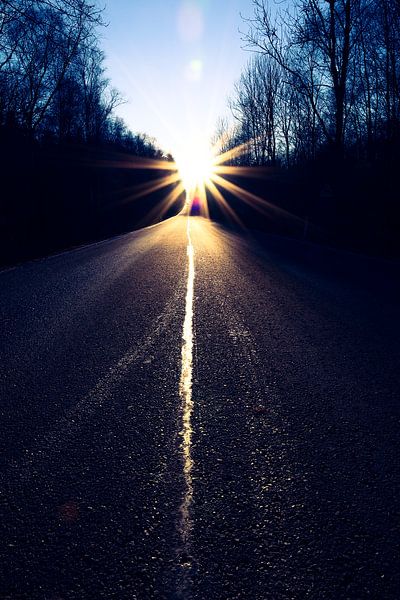
Buy the photo Sun Road. by PEEQ. on canvas, ArtFrame, poster and wallpaper, printed on demand in high quality.
About "Sun Road."
by PEEQ.
About the artwork
The sun is the star closest to Earth and the center of the solar system. The sun is a medium-sized star in an outer arm of the Milky Way galaxy. Seen from Earth, the sun is by far the brightest object in the sky; therefore, the sun determines the usual distinction between day and night. The sun is responsible for the vast majority of heat in Earth's atmosphere and is the main source of energy for life on Earth.
The sun is classified as a dwarf star (yellow dwarf). The sun developed about 4.6 billion years ago and is now midway through the main sequence. The sun is composed of very hot plasma. It contains over 99% of the solar system's matter, mostly hydrogen and helium. The inner part of the sun is so hot and dense that nuclear fusion takes place: every second, about 600 million tons of hydrogen are converted into helium. Most of the energy formed in the process is emitted in the form of radiation, including visible light. The surface of the sun shows a varying number of sunspots, which are caused by local magnetic fields that inhibit convection.
In a few billion years, the sun will enter its next phase of development. The hydrogen within the solar core will run out, causing the core to collapse under its own weight. The sun will then increase in heat and size (red giant), swallowing Venus and Mercury and making Earth uninhabitable in the process. At the end of its life cycle, the sun will release its outer layers (planetary nebula phase) and transform into a white dwar

About PEEQ.
I walk, I stop, I look, I click... Read more…
 Netherlands
Netherlands Ordered in May 2017
Ordered in May 2017

 Netherlands
Netherlands Ordered in October 2021
Ordered in October 2021
 Netherlands
Netherlands Ordered in January 2022
Ordered in January 2022
 Netherlands
Netherlands Ordered in January 2019
Ordered in January 2019
 Germany
Germany Ordered in October 2024
Ordered in October 2024
 Germany
Germany Ordered in January 2020
Ordered in January 2020
 Germany
Germany Ordered in May 2021
Ordered in May 2021
 Netherlands
Netherlands Ordered in January 2023
Ordered in January 2023
 Germany
Germany Ordered in February 2021
Ordered in February 2021
 Germany
Germany Ordered in November 2020
Ordered in November 2020
 Netherlands
Netherlands Ordered in January 2022
Ordered in January 2022

 Netherlands
Netherlands Ordered in March 2020
Ordered in March 2020
About the material
Canvas
A classic and timeless material
- Fine-art print quality
- Frame made of sustainable wood
- Durability of minimum 10 years
- Available with floater frame
Discover the artworks of PEEQ.
 Loenen on the Veluwe.PEEQ.
Loenen on the Veluwe.PEEQ. Furkapas.PEEQ.
Furkapas.PEEQ. Mariënwaerdt.PEEQ.
Mariënwaerdt.PEEQ. Iseltwald.PEEQ.
Iseltwald.PEEQ. Sunrise.PEEQ.
Sunrise.PEEQ. Lighthouse.PEEQ.
Lighthouse.PEEQ. Ouddorp.PEEQ.
Ouddorp.PEEQ. Sunset.PEEQ.
Sunset.PEEQ. Dunes.PEEQ.
Dunes.PEEQ. Fallen.PEEQ.
Fallen.PEEQ. Culemborg.PEEQ.
Culemborg.PEEQ. From Above.PEEQ.
From Above.PEEQ. Tennis Court.PEEQ.
Tennis Court.PEEQ. Floodplains.PEEQ.
Floodplains.PEEQ. Saeftinghe.PEEQ.
Saeftinghe.PEEQ. Drowned Land.PEEQ.
Drowned Land.PEEQ. Blanket of fog.PEEQ.
Blanket of fog.PEEQ. Mysterious Nature.PEEQ.
Mysterious Nature.PEEQ. Ecoduct.PEEQ.
Ecoduct.PEEQ. Abstractor.PEEQ.
Abstractor.PEEQ.













 Ardennes
Ardennes Astrology and Space
Astrology and Space Belgium
Belgium Europe
Europe Photo wallpaper
Photo wallpaper Photography
Photography Serene Peace
Serene Peace Sun
Sun Sunset
Sunset Trees
Trees